Outdated or Unsupported Browser Detected
DWD's website uses the latest technology. This makes our site faster and easier to use across all devices. Unfortunatley, your browser is out of date and is not supported. An update is not required, but it is strongly recommended to improve your browsing experience. To update Internet Explorer to Microsoft Edge visit their website.
To qualify for Unemployment Insurance (UI), you must:
If you were paid UI in a prior benefit year which has ended, you must have worked since the beginning of that benefit year and earned at least eight times the weekly benefit rate of that claim.
Even if you have earned sufficient wages from covered employment to meet the qualifying wage requirements listed above, you must meet other criteria to be paid UI. See Eligibility Issues for more information.
Base Period: The first four of the last five completed calendar quarters prior to the filing of your initial claim application for UI for a new benefit year. Wages from this base period are reviewed to determine UI eligibility. If you do not have enough wages to qualify for UI using this base period, an "alternate base period" will be used. The alternate base period is the first four most recently completed calendar quarters prior to the week you filed your initial claim application for UI for a new benefit year.
The following chart will help you understand how we determine the calendar quarters in your base period. The four shaded quarters in each row are the base period quarters for a claim started in the far-right quarter of the same row.
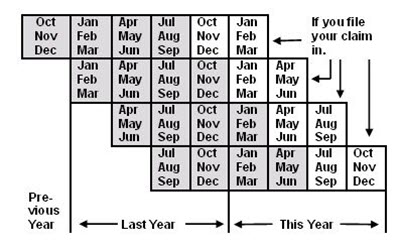
Interactive calculator: https://dwd.wisconsin.gov/uiben/calculators.htm.
Put in the date your claim would start to determine which quarters will be used.
Covered Employment is work you performed for an employer subject to unemployment insurance law. Wages earned from covered employment are used to calculate your benefit rate and the total amount of benefits available.
Wages earned from excluded employment cannot be used to qualify for UI and will not affect your benefit rate or the total amount of benefits available. However, you may be required to report wages earned from excluded employment when you file weekly claims. See Reporting Earnings for more information.
Some examples of excluded employment include employment:
Note: If a worker has been performing services for pay for an employer, there is a presumption in the law that the worker is an employee and not an independent contractor. If a worker is under the control or direction of the employer, they may be considered an 'employee' for the purposes of UI. See dwd.wisconsin.gov/worker-classification/ui for additional information.
Qualifying Wages: Wages from covered employment paid in the base period which equal or exceed the amount required establish a benefit year.
Weekly Benefit Rate (WBR): Your calculated weekly benefit rate is the maximum amount of UI that can be paid to you for any week that you are eligible for UI.
Your WBR will be 4% of the wages you were paid during the highest-paid quarter of your base period. If your WBR is less than $54, you do not qualify for UI. The maximum WBR is $370.
Use the Weekly Benefit Rate Chart to determine your weekly benefit rate based on your high quarter wages.
Benefit Year: The 52-week period that begins the week your initial claim application is filed. The maximum benefit amount computed from wages paid during the base period can be paid to you for the weeks you are totally or partially unemployed during your benefit year. If the maximum benefit amount is all paid to you before your benefit year ends, you are not eligible for UI for any remaining weeks you are totally or partially unemployed during your benefit year.
Maximum Benefit Amount (MBA): Your MBA will be 26 times your WBR or 40% of your total base period wages from all covered employment – whichever is smaller. Your MBA is like a checking account balance. As you are paid UI during your benefit year, the amount paid is subtracted from your MBA balance until it reaches 0. If you are paid your full MBA before your benefit year ends, no benefits can be paid to you for the remainder of the benefit year, even if you remain unemployed. Once your benefit year ends, any remaining MBA balance from that benefit year can no longer be paid to you. However, if you are still unemployed after the end of your benefit year, you can file another initial claim application to start a new benefit year based on wages paid during the new base period for your new claim.